Delirium – Non-delirium etiologies of Altered Mental Status
Remember that the development of delirium is thought to depend on the vulnerability of the patient (predisposing factors) and the magnitude of the noxious stimuli and insults (precipitating factors).
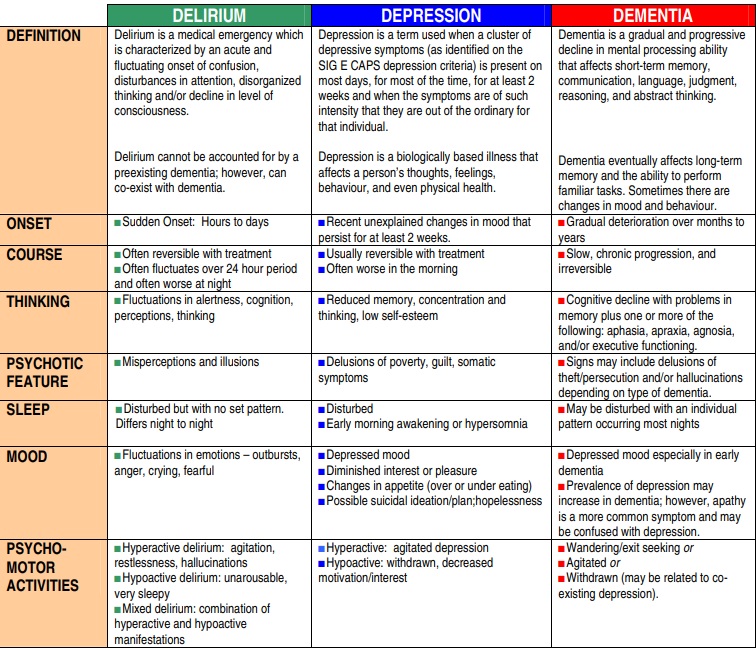
In the event, the patient clearly does not have delirium but does have a change in mental status, below are differential diagnoses. Of note, the 3Ds — delirium, dementia, and depression — are thought to be common mimics. When in doubt, assume delirium while ruling out other etiologies.
Dementia
Dementia is a slow progressive cognitive decline that causes acquired impairment in instrumental and non-instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs/ADLs). Unlike delirium, attention is generally preserved with some exceptions (namely Lewy Body Dementia).
Primary psychiatric illness – depression
Consider primary depression, mania, or psychosis
“Sundowning”
“Sundowning” is poorly understood phenomenon where patients with dementia have a known pattern of worsening behaviors (should precede hospitalization)
Post operative cognitive dysfunction
Post operative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a clinical syndrome where cognitive performance drops after surgery. POCD is an area of ongoing research
Source: Berger M, Nadler JW, Browndyke J, et al. Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction: Minding the Gaps in Our Knowledge of a Common Postoperative Complication in the Elderly. Anesthesiol Clin. 2015;33(3):517-550. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2015.05.008
Sedation from medications
Such as somnolence from opioids, benzodiazepines, muscle relaxants, anticholinergics, or anesthesia
Seizures
Particularly non-convulsive status epilepticus